Day :
- Oral Microbiology and Pathology
Session Introduction
Akash Akinwar
Periodontist & Implantologist (GDC &H Mumbai), India
Title: Mobile Dental Photography for Dental Documentation
Biography:
Dr. Akash Akinwar completed his post-graduation in Periodontics & Implantology from Government Dental College & Hospital (GDC & H) Mumbai in the year 2007 and since then he is completely into private Dental Practice focusing Periodontics, Oral surgery & Implant Dentistry. He is a consultant Periodontist & Implantologist at various private Dental Clinics & Hospitals in & out of Mumbai. Since last 13 years, he has performed more than 4000 various surgical procedures including Periodontal, Oral Surgical & Dental Implants. He has won several prizes in the best paper category in various national conferences. He has more than 47 International, National & State level scientific publications to his credit all together. He has organized many Implant, Mobile Dental Photography & Practice Management Workshops for private practitioners, BDS & MDS students. He is recipient of “BEST IDA MEMBER” (National Award- Dr. Ratan H. Doctor award) in the year 2007-08. He has been nominated for “ME MUMBAIKAR AWARD” in the year 2009-10. He is a recipient of recipient “OUTSTANDING DENTIST OF THE YEAR” (Highly commended) award by Famdent in the year 2014. He is a recipient of “ORAL & MAXILLOFACIAL PATHOLOGY” award at International Case Report Conference “SHOWCASE 2015” at Chennai. Recipient of “Implantologist of the Year 2016 (Special Jury Award)” by Famdent in December 2016. He has Co-Authored a textbook of Clinical Dentistry titled “Clinical Fixed Prosthodontics” in the year 2017 Authored by Dr. Moez Khakiani. Till date he has trained and mentored more than 600 Dental Practitioners for Implant placement. He is the pioneer of Mobile Dental Photography (MDP) and Only Mentor of MDP in India. He has worked as a Mentor for Adin Implants India. He had worked as a Mentor for Diploma in Advance Implantology at the University of Bucharest, Romania. He is a passionate Macro Photographer, Snake rescuer & an adventurist. He is always involved into various adventurous activities like Forest Walks, Sky diving, Scuba diving, Trekking & Wildlife Photography. He is a Licensed Scuba Diver registered with International Scuba Diving Association PADI. He has many macro & wildlife publications in the National & International photography magazines like Save Us, Lonely Planet etc. His Macro images have been exhibited in various reputed exhibitions by DCP & MID-EARTH.
Abstract:
Dental Photography has become an integral part of clinical practice for legal, clinical & academic purpose. Photography & Documentation goes hand in hand and have been proven as the most powerful tool of convincing patient in clinical practice. In the Era of Smartphone, which is supposed to be very handy & convenient equipment; using mobile camera one can take absolutely sharp & clear images of the particular case.
Mobile Photography is becoming one of the fastest & easy ways to record or document clinical cases. This session will help practitioners to understand the use of Mobile Camera for recording day to day cases in a very convenient & easy way. Dr. Akash Akinwar has been documenting clinical cases with mobile camera since last 8 years and has more than 44 publications and many hundred well documented cases of Periodontics, Oral Surgery & Implant Dentistry. His aim is to motivate & teach Graduates, Post graduates & Practitioners to document cases which have many fold benefits in the clinical practice.
This lecture is a simplified and informative session that empowers Graduates, Post graduates & Practitioners to document their work using Smartphone (Mobile) camera.
So come & learn the tips & tricks of Mobile Dental Photography.
Abdullah Abdul Rida Abdullah Alajmi
Otago University, New Zealand
Title: White lesions of the oral mucosa: iOS Apple smartphone App
Biography:
Studied BDS in Otago University in New Zealand. Studied 2 years of BSc major in Anatomy in the same University. Successfully passed Membership Examination (MFD) by the RCSI. Worked as a tutor in iOS App development in Otago University. Since 2012 onwards trying to link technology with dentistry through smartphone iOS Apps. This topic was presented three times in different occasions in Sultanate of Oman: Oman’s 18th international dental conference, Royal hospital medical libraries symposium, and creative & innovative Learning Strategies in Higher Education. Workshop presented in the presence of the Ministry of Health minister.
Abstract:
Objective: The purpose of this study was to plan, design, build and test a prototype iOS iPhone App to aid general dentists in their diagnosis of oral white lesions.
Methods: Twenty-two oral white lesions were listed under seven categories: hereditary, infectious, traumatic, immunological, idiopathic, potentially malignant and malignant. Lesions were grouped according to similarities and differences in tables. Five questions are considered the gold standard for obtaining differential diagnoses for any lesion. Two examples of the method were presented in graphs using ‘yEd Graph Editor’ and then used in the i-diagnostic tool App. The App consists of simple Table View Controllers, linked using push segues and was created using Xcode 5.0 on Macbook OS X version 10.8.4, 2.5 GHz Intel Core i5, and 4 GB 1600 MHz DDR3 Memory. The App was optimized to work on iOS 7.0 software. A System Usability Scale (SUS) test was performed by five general dentists from the Faculty of Dentistry at the University of Otago.
Results: The average SUS result was 84. On a 5-point Likert scale, all five usability testers reported 4 (“agree”) to the question “I would use this App in a clinical setting”. Further feedback and suggestions included; difficulty assessing lesion texture from the digital photographs, more options for the site of lesion required, variation in assessment when selecting colour, the difference between solitary and multiple sites.
Conclusion: Overall the SUS result is satisfactory at this stage of the i-diagnostic tool development. Further development of the App, along with usability testing, is required to achieve better functionality, accuracy, reliability and a more user friendly tool.
Ahmed Abosabaa
Delta University for Science and Technology, Egypt
Title: The effect of two different solitary attachments used to retain implant assisted mandibular distal extension Removable Partial Overdenture on abutment alveolar bone height changes
Biography:
Ahmed Mohamed Amr Abdelmoez Abosabaa had Bachelore degree from the faculty of dentistry , Tanta university in 2009 . Became member of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh in 2012 after passing MFDS exam and doing Masters degree in Prosthodontics department , Mansoura University which is based on Implant Assisted partial overdentures.
Abstract:
Objectives: This clinical comparison study compared between different designs of solitary attachments used to retain implant assisted mandibular distal extension RPD regarding alveolar bone height changes around abutment teeth.
Methods: Twelve patients with mandibular Kennedy Class I were selected for this study. The remaining natural teeth were extended from the first premolar on one side to first premolar on the other side. one implant was placed in each first molar region bilaterally. The removable partial dentures were retained anteriorly by RPA clasp design and posteriorly either by ball attachment (group I) or by OT-equator attachment (group II) . Alveolar bone height changes around the primary tooth abutments were radiographically evaluated using cone beam volumetric CT.
Results: Regarding bone loss around the primary abutment teeth, Ball attachment group (0.72 ± 0.15) significantly (p value = 0.008) showed less crestal bone resorption when compared to OT-equator attachment group (1.01 ± 0.25).
Conclusion: Within the limitation of this study and regarding the preservation of abutment teeth, the use of ball attachment may be the suitable choice for anchoring distally extended removable partial denture to dental implants with improved longevity of the natural tooth abutments.
Clare Lowe
Newcastle Dental Hospital, United Kingdom
Title: Adequate completion of radiology request forms at Newcastle Dental Hospital. (A two-cycle audit)
Biography:
Clare Lowe is currently in the first year of her Dental Core Training at Newcastle Dental Hospital. She graduated from the University of Aberdeen in June 2016 with a Bachelor of Dental Surgery degree, and then went on to complete the diploma of Membership to the Faculty of Dental Surgery of the Royal College of Surgeons of Edinburgh in November 2017.
Abstract:
Objective: The usefulness of a radiological examination and its report can be reduced significantly if the clinical background and specific problem to be answered is not given in the request. Inadequate information can lead to mistakes in patient identification and delay in returning reports to the correct destination. The aim of this audit was to assess current request forms to determine if sufficient information was provided. The audit aims to ensure the quality of care provided to patients, and to identify ways to assist clinicians to provide adequate information when requesting a report.
Methods: Data was randomly collected from 53 patient records where a radiological request was made from the Oral Surgery department using the current request forms. Forms were analysed against eight criteria and recorded as either ‘criteria met’ or ‘criteria not me’. Data was recorded on a collection table and analysed to determine what percentage of radiology request forms could be deemed ‘adequate’, and when not, what were the failing criteria? A new form was then constructed considering the failings of the first cycle of data collection. The new radiology request form was then used for a period of 3 months and a second cycle of data collected.
Results: The first cycle of the audit revealed that 0% of request forms met the standard set, with 100% of forms omitting at least one of the criteria measured. Following the implementation of the redesigned form, the second cycle revealed that 70% of all forms met all criteria and could be deemed as adequate.
Conclusion: The new request form has dramatically improved the way the forms are completed. Marked improvement was noted in the information provided by clinicians on the new forms, showing that the new design helps to prompt clinicians to provide adequate information for reports to be generated.
Nima sabzchamanara
National medical university, Bogomolets. Kiev, Ukraine
Title: Periodontal muscle training can strength the periodontal support, Fit your teeth
Biography:
Abstract:
Statiatical analysis, A total of 505 patients in general practice were asked to respond to a list of 25 obligatory nourishment for a child while going to have the first teeth, for its effectiveness in dealing with patient's periodontal health especially include chewing hard food. They were also asked to select the three effective nutrition for periodontal tissue. The indicts of patient perceived importance of the periodontal health were derived and each compared with actual effectiveness as determined from a sample of 250 patients opinion. Although the majority of patient's 18 of 25 nutrition as being very effective, there was no significant association with patient perceived nourishment effectiveness and actual effectiveness. The implications for patient training are discussed.
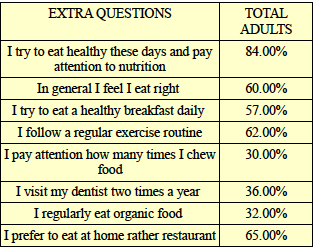
Introduction: By comparing the effect of long term workout in the fitness gyms and the habit of consuming hard rational food daily with a weekly schedule, could be very likely and would be support the oral health indeed. What to do to have aesthetically and functionally prevention method for further gum and periodontal diseases, which could be less aggressive and conservative, cheap and home treating methods. In case one cares about his body's physique, also he can care about the Gum structure as well.
Materials and Methods: To have a review, Bundles attached to teeth and their dis attachments provoke further injuries. Let's take a look at these bundles, if we peel away alveolar septa and papillae & marginal part, we can see the bundles (periodontal ligament), (1) which is composed of bundles of connective tissue's fiber that anchor the teeth within the jaw. Each bundle is attached to cementum covering the root of the tooth. The other end is embedded in bony tooth sockets (alveolar socket). These bundles of fibers allow the tooth to withstand the forces of biting and chewing. Endomysium, the connective tissue sheaths that surround each skeletal muscle fiber separating the muscle cells from one another. It also contains capillary nerves and lymphatics. As an illustration, Organization of skeletal tissues, Intact skeletal muscle. Biceps bra chi are attached to bones through tendons.connective tissue. The entire muscle is surrounded by connective tissue called epimysium.(2) The muscle is organized into bundles called premium. Each fascicles contains many individual fibers surrounded by connective tissue called Endomysium. In some muscles there might only be relatively few fibers such as in muscle of the eye in which these are only 10 of fibers. In some of the bigger muscles in the body there may be thousands of fibers, for instance, there can be up to 400000 fibers in the bicep muscle in front of the arm. Each of these fibers is surrounded by sheaths of fibrous tissue membrane or fascia called Endomysium (endo- means within). Therefore, by having regular training in fitness centers our extremities muscles can strength and can have an aesthetic and supportive function for skeletal system.
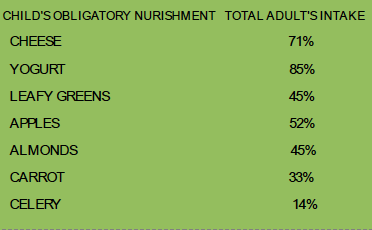
Results: As within skeletal growth, the muscles in the body also grow at irregular rates. The enlargement of muscles (hypertrophy) makes them thicker but muscle fibers can also get longer. With certain types of training and genetics, muscle mass can change.(3) According to the aging of muscular system, one reason is reducing the strength and power of the muscles, therefore, by training the endomysiums within the periodontal ligament with special training as well as eating hard foods and chewing them we can train them exactly like fitness club. The experiment above 18-25% of those patient who had answered to the test satisfactory had a healthier gum structure in comparing with the unsatisfactory ones. By making some clinics besides gyms and sport centers which prescribe daily,weekly,monthly schedules to fit the gum muscles with special measurement individually for each patient can make a revolution in gum and oral health history.
Conclusion: Due to the proper nourishment for the newborn babies we acknowledge that they are effective to form the jaws, gums, teeth, and help them nourish well and form the proper shape. Therefore, repeating this process could be an aid for preventing any lack of support or lease to make further diseases as these nutrition only strength the body mass around teeth.
- Oral Medicine
Session Introduction
Smriti Jagdhari Golhar
Vidhya Shikshan Prasarak Mandal’s Dental College & Research Institute, Maharashtra
Title: Different treatments modalities in MPDS with cervical pain patients - A Prospective Study
Biography:
Dr.Smriti Jagdhari Golhar (MDS) is working as an Assistant Professor in Department of Oral Medicine & Radiology, Vidhya Shikshan Prasarak Mandal’s Dental College & Research Institute, Nagpur, Maharashtra. She has published her research work and Case Reports in International and National Journals. Her extensive research focuses on Myofascial Pain Dysfunction Syndrome and Cervical pain, morphological type of soft palate in Obstructive Sleep Apnoea patients, Awareness of Oral Cancer in General Population and role of Astaxanthin in the management of Oral Submucous Fibrosis. She has reviewed research articles in esteemed journals.
Abstract:
Abstract- Aim: The aim of this study was to find out the therapeutic correlation between cervical dysfunction and myofascial pain dysfunction syndrome (MPDS).
Materials and methods: The study included 46 patients out of which 23 had MPDS with cervical pain (group I), and 23 patients had only MPDS (group II). Detailed history and examination of the patients were carried out, and the factors taken into consideration were pain and tenderness of muscles of mastication and neck muscles, maximum comfortable mouth opening, and cervical range of motion. All the patients were randomly divided and advised physical exercises, light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation (LASER) therapy, and the combination of both exercise and LASER. Patients were assessed for the relief of signs and symptoms of myofascial pain and cervical pain post treatment, every month for 2 months.
Results: Both the groups showed a similar response to all the different treatment modalities. In group I, the patients also had relief in their cervical pain although the treatment was directed for MPDS. Patients from both the groups who were advised LASER and combination of both exercise and LASER showed better response in terms of reduction in visual analog scale, number of tender muscles, and increased maximum comfortable mouth opening post treatment and during the follow-up, as compared with the patients who were advised only exercise.
Conclusion: Patients having cervical pain showed significant improvement comparable with patients having no cervical pain. Hence, the conclusion drawn was that the combination of both the modalities was better to treat cervical and MPDS pain.
Faisal Al Rumaihi
Prince Sultan Military Medical City
Title: Case Report of Impacted Bilateral Mandibular Fourth Molar
Biography:
Al Rumaihi Faisal has completed his BDS in 1988 in King Saud University in Riyadh KSA and Residency program at RKH Hospital 1989 advance certificate in restorative and cosmetic dentistry in 1995 at Boston University, USA and Ph.D degree at Boston University Goldman School of Graduate Dentistry USA. He is consultant restorative in dentistry in Prince Sultan Military Medical City in Riyadh. He is director of Restorative section in dental clinic and have a years of teaching and clinical supervision experience.
Abstract:
Supernumerary teeth is a rare dental anomaly in maxilla and mandible can be classified by shape and by position in the jaw. It might cause complication such caries, perio dental disease, and delay or impaction of permanent teeth.
Supernumerary tooth or hyper dontia is not as common as hypodontia. The prevalence in primary dentition .2 to .8 % and in the permanent dentition .5 to 5.3% with geographic variation.
The fourth molar is a kind of super numerary tooth they have been classified as a type of paramolar or disto molars tooth.
This case report of a 20 years old female pt. (Medically fit) come to the dental clinic complaining from pain in the lower right quadrant upon clinical examination and routine radiographic examination revealed impacted third molar and un erupted bilateral mandibular fourth molar orthopantogram (OPG) xray should this rare case of un erupted bilateral disto molar in mandible without any associated syndrome. This case report discuss the diagnosis and treatment of this rare case of impacted bilateral mandibular disto molar and in what condition shall we keep the fourth molar or extracted.
Mitali Gandhi
Dr. D. Y. Patil University,Navi Mumbai, India
Title: A To Z Of Creating Perfect Provisional Restorations In Fixed Partial Dental Prosthesis
Biography:
Dr. Mitali Gandhi has completed her Bachelors in Dental Surgery (B.D.S) from D. Y. Patil University , Navi Mumbai and went on to complete her Masters in Oral & Maxillofacial Prosthodontics & Oral Implantology from the same university. She maintains 2 successful private practices and also a centre dedicated to Dental Education in Mumbai. She is a consultant Prosthodontist & Implantologist to several private practices and also to the biggest dental chain of clinics in India (Sabka Dentist). She is associated with several charitable causes for beautification of smiles in young girls. She also has scientific papers to her credit.
Abstract:
Beauty is power, a smile is it’s sword. As a dentist, there is nothing more satisfying than creating beautiful and radiant smiles. However, a lot of dental procedures involve multiple visits to the dental office to achieve that perfect end result. The role of a provisional restoration in fixed prosthodontics cannot be overemphasized. Provisional restorations must satisfy requirements of pulpal protection, positional stability, occlusal function, oral hygiene, margin accuracy, wear resistance, strength and esthetics. They serve as a great tool in fabrication of final restoration once they have been evaluated intraorally. They also promote guided tissue healing to achieve better emergence profile. Most importantly, they restore the patient’s confidence!
A well made provisional should provide a preview of the future prosthesis and enhance the health of the abutments and periodontium. Fabrication of a perfect chairside provisional requires skill. The different methods of provisionalization are:
- Direct method
- Indirect – direct method
- Indirect method
The workshop is designed to include the following topics :
1) Demonstration & Hands-On Of Fabrication Of:
a) Esthetic anterior provisional restoration for crown and bridge (designing of ovate pontic).
- Posterior provisional restoration for bridge.
2) Different materials & techniques of fabrication of provisionals.
3) Occlusal adjustments in static & dynamic occlusion.
4) Finishing & polishing protocols.
5) Cementation of provisional restoration.
6) Management of provisional restoration shortcomings.
7) Clinical cases of provisionalization.
- Oral and Dental Health|Oral Medicine|Dental Surgery|Dental Nursing|Cosmetic Dentistry |Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | Geriatric Dentistry | Dental Anaesthesia |Nano Dentistry
Location: Dubai, UAE
Session Introduction
Lisha Gangwal
India
Title: Be a pain-free dentist: Posture matters
Time : 11:30-12:00

Biography:
Abstract:
Khalid Mohammed Idrees
King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Center, Saudi Arabia
Title: Endodontic flare-up Khalid Mohammed Idrees,
Biography:
Abstract:
Shaeesta Khaleel Ahmed B
King Khalid University, Saudi Arabia
Title: Way to an aesthetic depigmented smile - The Cryosurgical avenue
Biography:
Abstract:
Josna Vinutha Yadiki
Al Jouf University, Saudi Arabia
Title: Initial ‘well-baby’ checkup for oral health: A cross-sectional study in Aljouf Province Saudi Arabia

Biography:
Abstract:
Smriti Jagdhari Golhar
Vidhya Shikshan Prasarak Mandal’s Dental College & Research Institute, India
Title: Different treatments modalities in MPDS with cervical pain patients-A Prospective Study

Biography:
Abstract:
Mallika Sethi
I.T.S-Centre for Dental Studies & Research, India
Title: Current clinical concepts in regenerative periodontal therapy

Biography:
Abstract:
Comparison of self nano emulsifying drug versus conventional drug in oral lesions and potentially malignant disorders
Sanjeev Laller, PDM Dental College and Research Institute, India
Title: Comparison of self nano emulsifying drug versus conventional drug in oral lesions and potentially malignant disorders

Biography:
Abstract:
- Workshop
Location: Dubai, UAE
Session Introduction
Dheyaa N Obada
University of Baghdad, Iraq
Title: Nanosurgical treatment for anterior teeth with large periapical lesion

Biography:
Abstract:
- Preventive Dentistry | Oral Microbiology and Pathology | Oral Implantology | Diabetes and Periodontal Disease | Electromagnetic waves and Dentistry | Endodontics and Restorative Dentistry | Dental education and Training | Regulatory and Ethical Issues of Dentistry
Location: Dubai, UAE
Session Introduction
Artemio Jr. LICOS,
Ilocos Training and Regional Medical Center, Philippines
Title: Child-to-child school health program (CtCSHP): Its impact on the oral health behavior of Grade 1 pupils in the division of La Union

Biography:
Abstract:
Samira Hosseini
Shahid Beheshti University of Medical Sciences, Iran
Title: Nano-Robots: Future revolution in dentistry
Biography:
Abstract:
Mouhibi Abdallah
Centre de Consultation et de Traitement Dentaire, Morocco
Title: Integrate occlusal analysis into your daily practice

Biography:
Abstract:
Mamta Malik
PDM Dental College and Research Institute, India
Title: Circulating Omentin-1-A new adipokine with diagnostic and therapeutic role in TMJ Disorders: Advanced endeavor to dental field

Biography:
Abstract:
Premila Selvi Suganthan
Annamalai University, India
Title: To lase, or not to lase integrating lasers to daily practice: A practical approach
Biography:
Premila Suganthan currently working as doctor in Chennai, India. She is the author of the several books and a well know doctor in india
Abstract:
- Workshop
Location: Dubai, UAE
Session Introduction
Lisha Gangwal
India
Title: Dental ergonomics…The key to a healthy dental career

Biography:
Abstract:
- Poster Presentation
